MuSACo - Multimodal Subject-Specific Selection and Adaptation for Expression Recognition with Co-Training
2026
- WACV 2026: IEEE Winter Conf. on Applications of Computer Vision, Tucson, Arizona, USA, 2026
Leveraging Multimodality for Personalized Expression Recognition
Published in WACV 2026: IEEE Winter Conf. on Applications of Computer Vision
🔍 Problem Overview
Personalized expression recognition (ER) involves adapting machine learning models to subject-specific data to improve recognition of expressions with considerable inter-personal variability. While Multi-Source Domain Adaptation (MSDA) can improve robustness by treating subjects as domains, current state-of-the-art methods often overlook multimodal information or blend sources into a single domain. This limits subject diversity and fails to explicitly capture unique subject-specific characteristics.
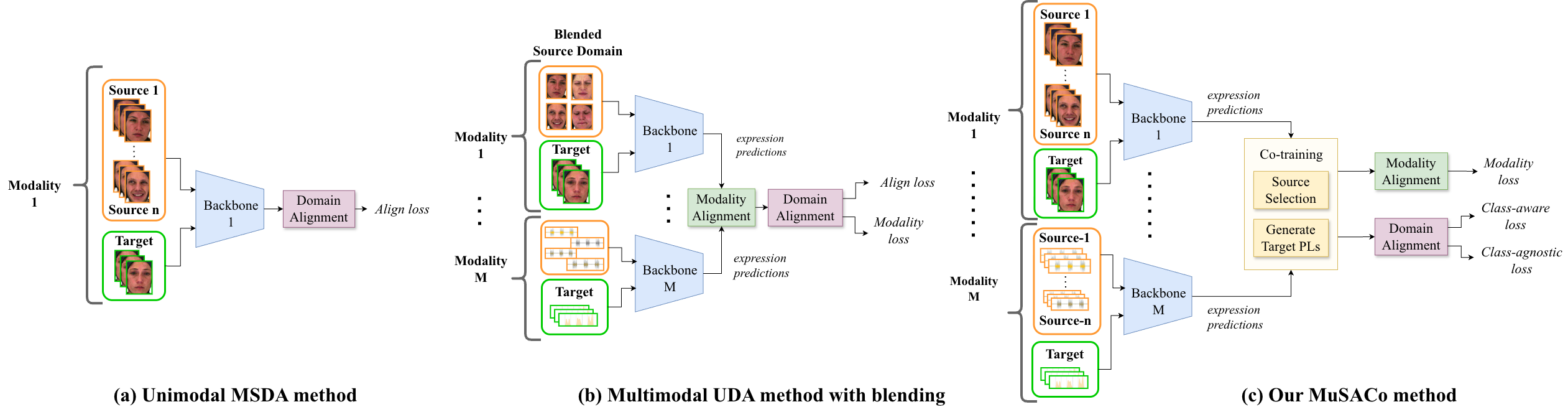
Figure 1 compares different approaches:
-
(a) Unimodal MSDA: Aligns sources within a single modality, which often reduces accuracy.
-
(b) Multimodal UDA (Blending): Blends sources into a single domain, failing to exploit subject-specific diversity.
-
(c) MuSACo (Ours): Selects relevant sources per modality using co-training and aligns them using both class-aware and class-agnostic losses.
Existing methods often fail to generalize for subtle expressions and across diverse individuals due to variations in cultural and individual expressiveness.
💡 Our Proposed Method: MuSACo
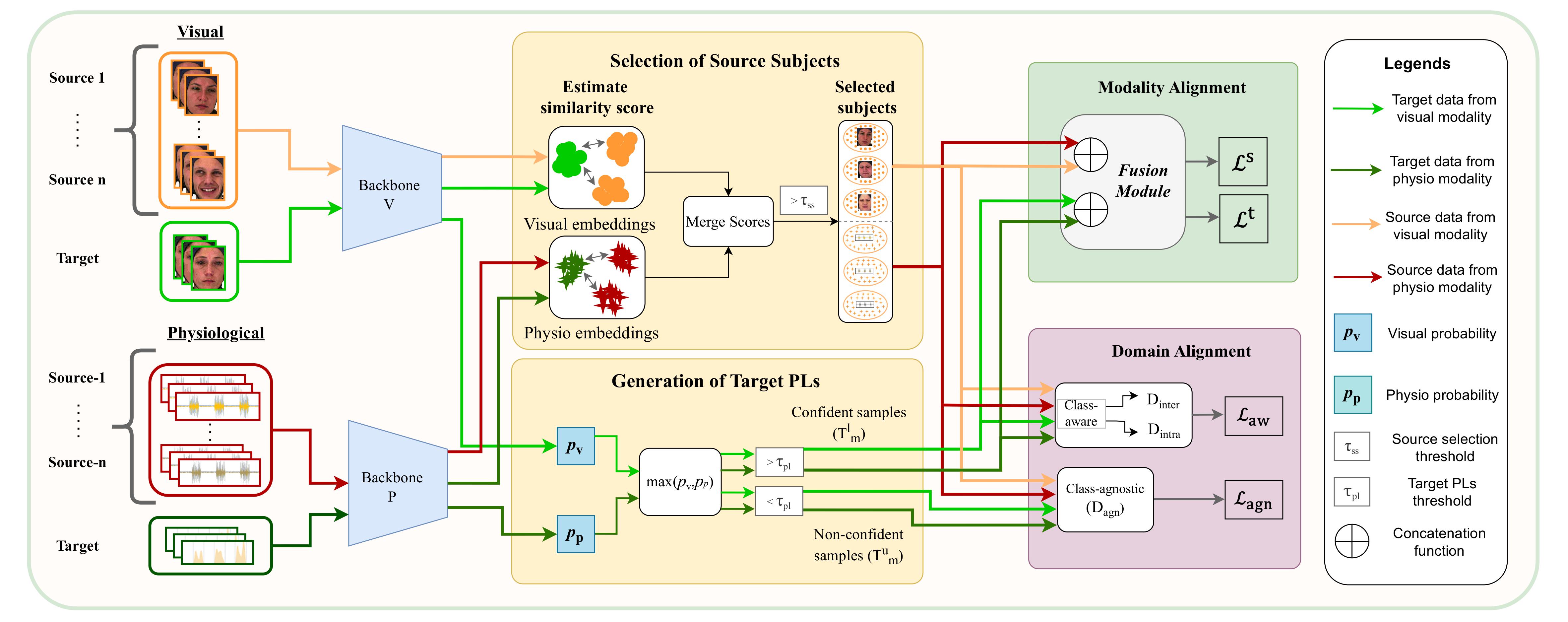
We introduce MuSACo, a Multimodal Subject-Specific Selection and Adaptation method based on Co-Training. It leverages complementary information across modalities (e.g., visual and physiological) and selects relevant source subjects for adaptation.
The method consists of three key stages
1️⃣ Source Selection via Co-Training
To address the challenge of leveraging multiple source subjects, MuSACo selects sources most relevant to the target.
- We estimate similarity scores between source and target subjects using embeddings from each modality.
- Using a co-training strategy, sources that produce high similarity scores in either modality are selected.
- A threshold is applied to filter out less relevant sources, ensuring only the most informative subjects are used.
2️⃣ Dual-Loss Domain Alignment
MuSACo employs a robust alignment process using target Pseudo-Labels (PLs):
✔ Generating Target Pseudo-Labels (PLs)
PLs are generated by selecting predictions from the dominant modality (e.g., visual or physiological) based on probability scores. This ensures diversity in feature representations.
✔ Class-Aware & Class-Agnostic Alignment
- Class-Aware Loss: We use confident target samples (selected via threshold) to minimize distribution mismatch through class-aware alignment.
- Class-Agnostic Loss: To utilize useful but less confident samples (which are often discarded), we introduce a class-agnostic loss that aligns non-confident target samples with the source.
3️⃣ Disentanglement & Fusion
To improve generalization:
Disentanglement: We use an entropy-based estimator (KNIFE) to disentangle identity-related information from expression-specific features.
Modality Alignment: Features from different modalities are concatenated for each selected source and confident target subject, then processed through a fusion module.
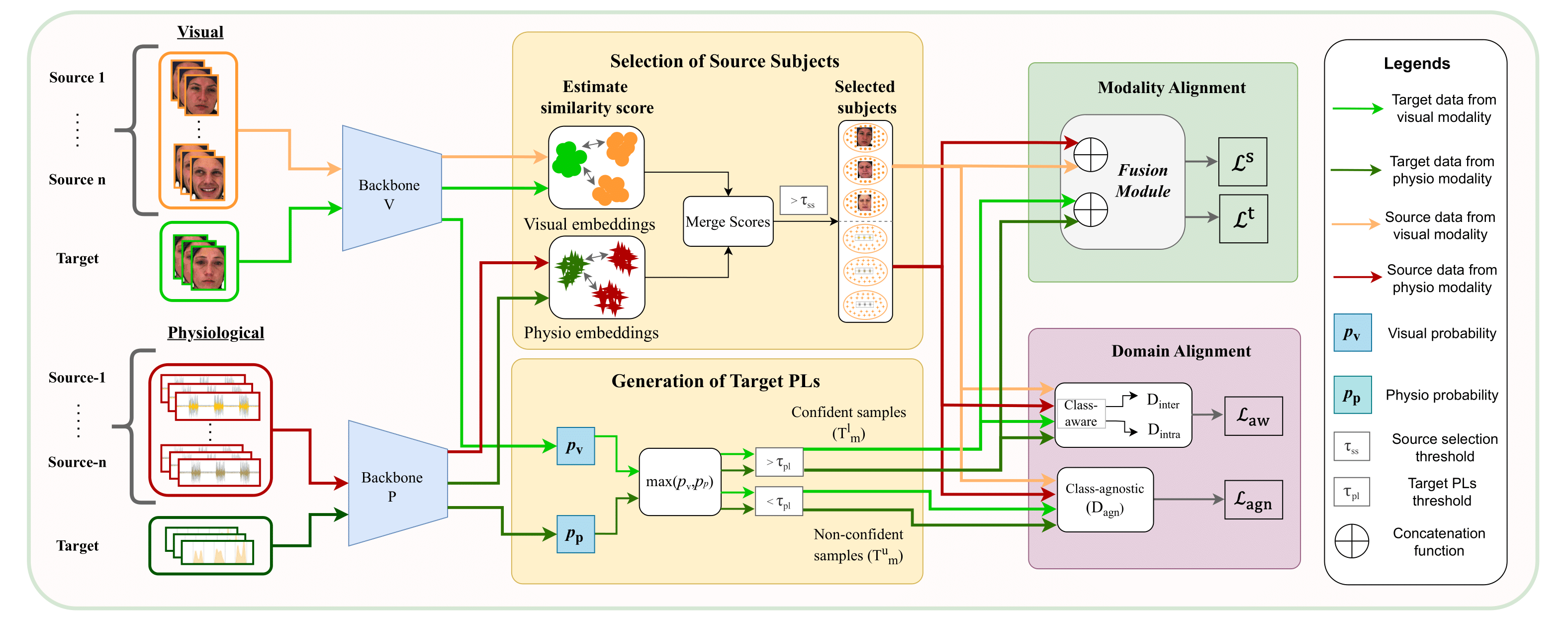
Overview of the MuSACo architecture, illustrating the co-training loop, source selection, and alignment modules.
📈 Results
We evaluated MuSACo on three multimodal datasets: BioVid (pain), StressID (stress), and BAH (ambivalence/hesitancy).
Key Findings:
- BioVid: MuSACo achieved 43.8% Avg Acc, outperforming Unimodal MSDA (34.7%) and Blended UDA (36.3%).
- StressID: Achieved an overall gain of 15.6% over the lower bound and consistently outperformed state-of-the-art MSDA methods.
- BAH: In uncontrolled, real-world settings, MuSACo surpassed all baselines, achieving 69.9% Average Acc.
MuSACo consistently outperforms UDA (blending) and state-of-the-art MSDA methods on challenging multimodal data.
✨ Takeaway
MuSACo supports personalized modeling by adapting to each target subject through relevant sources. This makes it particularly relevant for digital health applications, such as patient-specific assessment for stress or pain.
📄 Full Paper
Title: MuSACo: Multimodal Subject-Specific Selection and Adaptation for Expression Recognition with Co-Training
Authors: Muhammad Osama Zeeshan, Natacha Gillet, Alessandro Lameiras Koerich, Marco Pedersoli, Francois Bremond, Eric Granger
Venue: WACV 2026: IEEE Winter Conf. on Applications of Computer Vision, Tucson, Arizona, USA
🔗 Read the paper: Link 💻 Code: GitHub MuSACo
📬 Contact
Feel free to reach out for discussion or collaboration!