Progressive Multi-Source Domain Adaptation for Personalized Facial Expression Recognition (P-MSDA)
2025
- IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2025
Bringing Personalization to Facial Expression Recognition
Based on our publication in *IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing
🔍 Problem Overview
Multi-source domain adaptation (MSDA) traditionally assumes using all available subjects as sources improves performance.
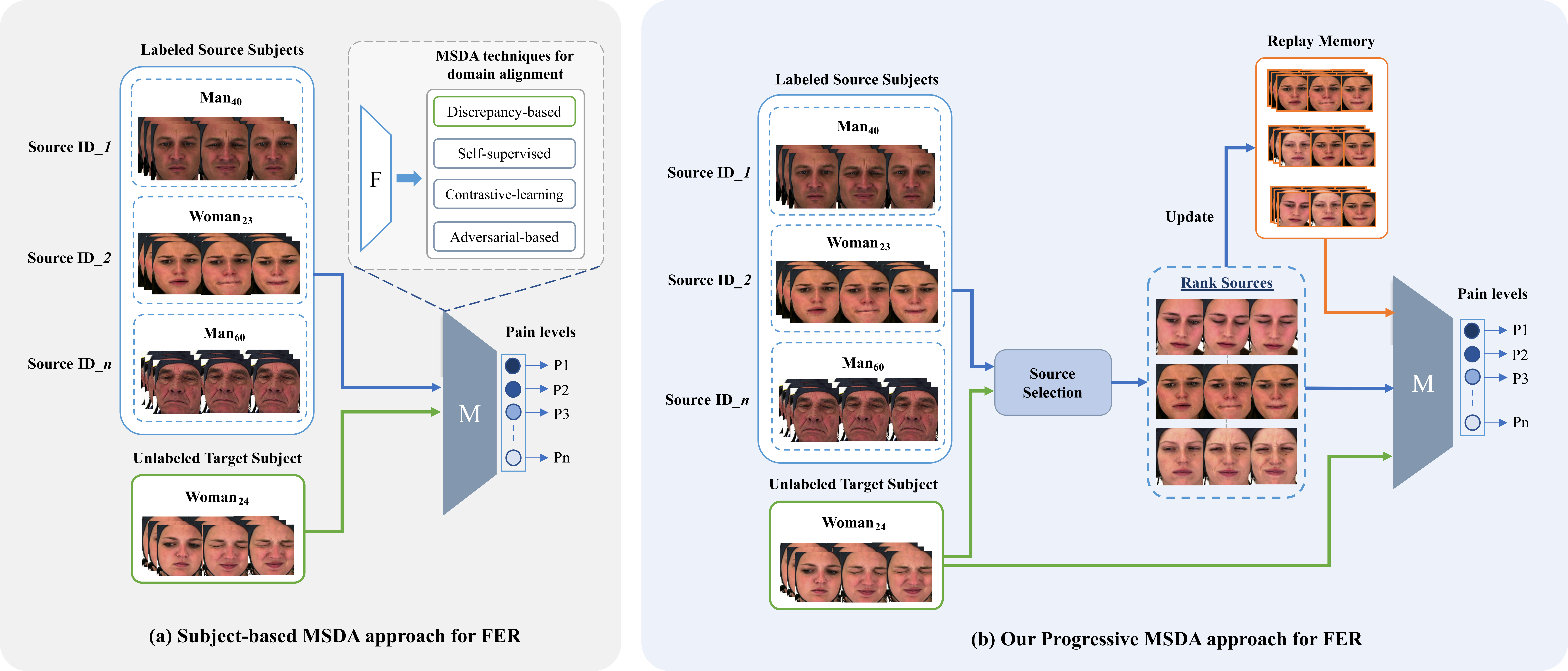
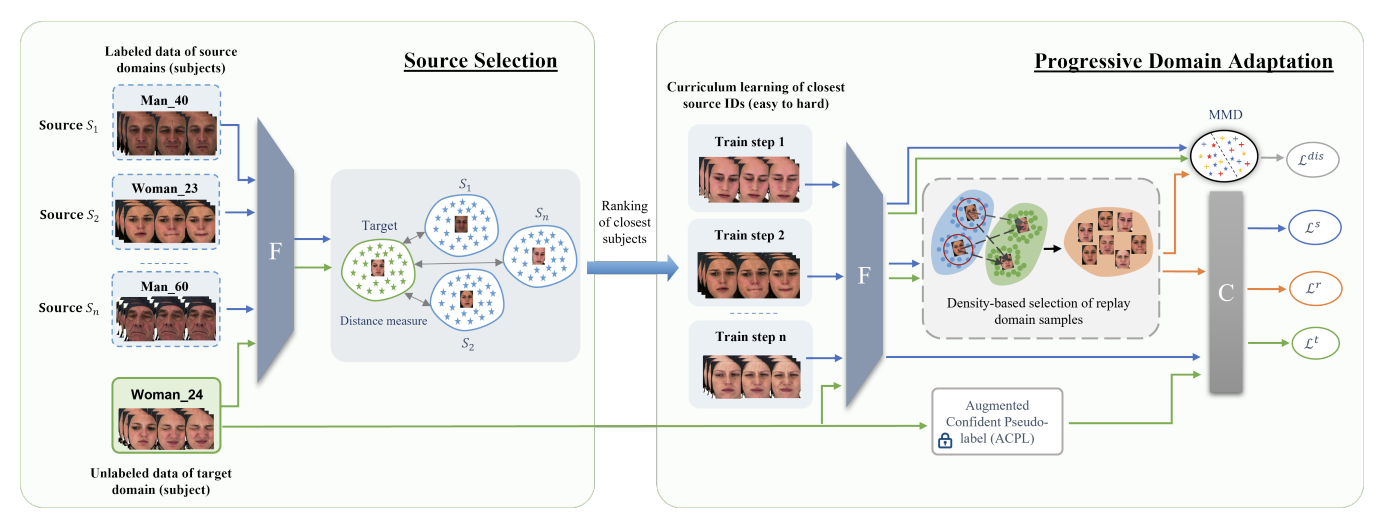
Figure 1 (a) illustrates:
- Large domain gaps between many source subjects and the target.
- Combining all sources introduces noise and negative transfer.
- Misaligned subjects confuse the model rather than helping it adapt.
Many source subjects lie far from the target in feature space — hurting adaptation.
This motivates our approach Figure 1 (b): ⚡ Start with the most similar subjects → gradually introduce more challenging ones.
💡 Our Proposed Method: Progressive MSDA (P-MSDA)
Our method consists of two major components:
1️⃣ Source Selection Using Similarity Ranking
We compute cosine similarity between the target subject and each source subject.
Sources are then ranked from closest → farthest.
This process is illustrated below:

Demonstrated how the model identifies subjects with the most similar expression distributions and facial structures, selecting them as the initial steps in the adaptation process.
These closest subjects form the basis for our curriculum:
- Step 1 → adapt to the closest subject
- Step 2 → adapt to the second closest
- …
- Step n → adapt to more diverse subjects
This progression greatly reduces early domain shift.
2️⃣ Progressive Domain Adaptation Pipeline
The complete workflow of P-MSDA:
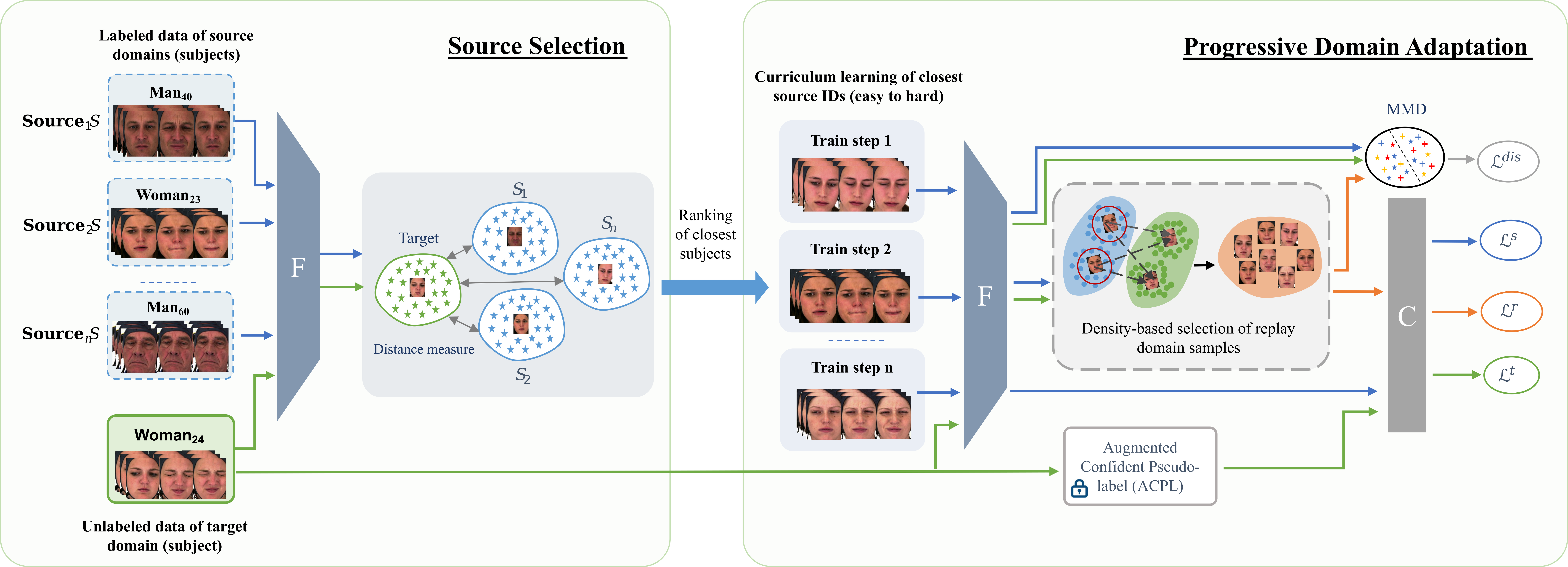
Key components:
✔ Progressive Curriculum
Subjects are introduced one at a time (easy → hard).
✔ Density-Based Replay Memory
At each stage, representative samples are stored based on cluster density — preventing forgetting.
✔ Multi-domain Alignment
Using MMD-based discrepancy loss, the model aligns:
- Current source
- Replay samples
- Target domain
This ensures stable learning at every stage.
📈 Results Across Benchmark Datasets
Our approach outperforms all MSDA and UDA baselines on:
- BioVid (Heat Pain database)
- UNBC-McMaster
- Aff-Wild2
- Behavioural Ambivalence/Hesitancy (BAH) dataset
Highlights:
- BioVid: 88% accuracy
- UNBC-McMaster: 0.88 accuracy
- Aff-Wild2: 0.46
- BAH: 0.71
- Cross-Dataset (UNBC → BioVid): 0.78
🎯 Why Progressive Learning Works
Ablations confirm:
- Random subject ordering performs significantly worse
- Density-based replay selection boosts stability
- Progressive alignment yields compact target-specific clusters
- Training efficiency stays high (only 3 domains used at once)
✨ Takeaway
P-MSDA enables robust, label-free personalization for FER systems:
- 🚀 Personalized FER without labeled target data
- 🔄 Scalable multi-source adaptation
- ❌ Avoids negative transfer
- 🏆 Achieves state-of-the-art results
📄 Full Paper
Title: Progressive Multi-Source Domain Adaptation for Personalized Facial Expression Recognition
Authors: Muhammad Osama Zeeshan, Marco Pedersoli, Alessandro L. Koerich, Eric Granger
Venue: IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing
🔗 Read the full paper here: IEEE Xplore Link
💻 Code: Github P-MSDA
📬 Contact
Feel free to reach out for discussion or collaboration!